A constant pressure (or isobaric) surface is a surface in the atmosphere where the pressure is equal everywhere along that surface. For example, the 100 millibar (mb) surface is the surface in the atmosphere where the pressure at every point along that surface is 100 mb. Since pressure decreases with height, the altitude of the 100 mb surface is higher than the 500 mb surface, which is likewise higher than 1000 mb. Meteorologists use pressure as a vertical coordinate to simplify thermodynamic computations which are performed on a routine basis.
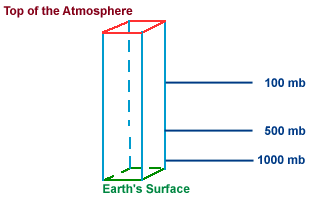
Measurements of the upper atmosphere (temperature, pressure, winds, etc.) are taken by instruments on weather balloons as they rise upward from the earth. When referring to the 500 mb surface, we mean a location in the atmosphere where the pressure has been measured to be 500 mb. The approximate heights and temperatures for several constant pressure surfaces have been listed below:
| Pressure | Approximate Height | Approximate Temperature | Sea Level 1000mb 850 mb 700 mb 500 mb 300 mb 200 mb 100 mb |
|
|
|---|
The atmospheric variables typically plotted on isobaric maps include: height of the pressure surface, temperature, moisture content and wind speed and direction.

isobars |
|

variation with temps |