|
|
. |
Cold Front
transition zone from warm air to cold air
A cold front is defined as the transition zone where a
cold air mass
is replacing a warmer air mass.
Cold fronts generally move from northwest to southeast.
The air behind a cold front is noticeably colder
and drier than the air ahead of it.
When a cold front passes through,
temperatures can drop more than 15 degrees within the first hour.
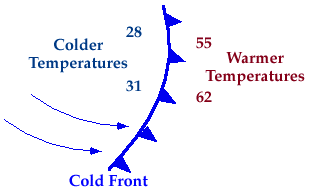
Symbolically, a cold front is represented by a solid line with
triangles along the front pointing
towards the warmer air and in the direction of movement.
On colored weather maps,
a cold front is drawn with a solid blue line.
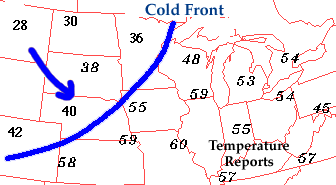
There is typically a
noticeable temperature change from one side of a cold front
to the other. In the map of surface temperatures below,
the station east of the
front reported a temperature of 55 degrees Fahrenheit while
a short distance behind the front, the temperature decreased to 38 degrees.
An abrupt temperature change over a short distance is a good indicator that
a front is located somewhere in between.
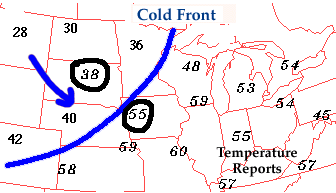
If colder air is replacing
warmer air, then the front should be analyzed as a cold front.
On the other hand, if warmer air is replacing cold air, then the
front should be analyzed as a
warm front. Common characteristics associated
with cold fronts have been listed in the table below.
|
|
Before Passing |
|
While Passing |
|
After Passing |
| Winds |
|
south-southwest |
|
gusty; shifting |
|
west-northwest |
| Temperature |
|
warm |
|
sudden drop |
|
steadily dropping |
|---|
| Pressure |
|
falling steadily |
|
minimum, then sharp rise |
|
rising steadily |
| Clouds |
|
increasing: Ci,
Cs and Cb |
|
Cb |
|
Cu |
|---|
| Precipitation |
|
short period of showers |
|
heavy rains, sometimes with hail, thunder and lightning |
|
showers then clearing |
| Visibility |
|
fair to poor in haze |
|
poor, followed by improving |
|
good, except in showers |
|---|
| Dew Point |
|
high; remains steady |
|
sharp drop |
|
lowering |
Table adapted from: Ahrens, (1994)
Fronts
|
|

wind shift
|
|




