Animation by: Bramer
Groundwater is all the water that has penetrated the earth's surface and is found in one of two soil layers. The one nearest the surface is the "zone of aeration", where gaps between soil are filled with both air and water. Below this layer is the "zone of saturation", where the gaps are filled with water. The water table is the boundary between these two layers. As the amount of groundwater water increases or decreases, the water table rises or falls accordingly. When the entire area below the ground is saturated, flooding occurs because all subsequent precipitation is forced to remain on the surface.
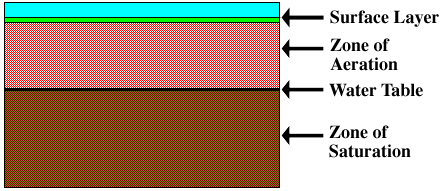
The amount of water that can be held in the soil is called "porosity". The rate at which water flows through the soil is its "permeability". Different surfaces hold different amounts of water and absorb water at different rates. Surface permeability is extremely important for hydrologists to monitor because as a surface becomes less permeable, an increasing amount of water remains on the surface, creating a greater potential for flooding. Flooding is very common during winter and early spring because the frozen ground has no permeability, causing most rainwater and meltwater to become runoff.
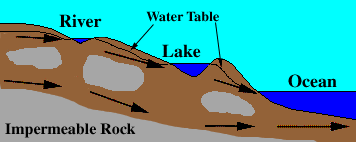
Water that infiltrates the soil flows downward until it encounters impermeable rock (shown in gray), and then travels laterally. The locations where water moves laterally are called "aquifers". Groundwater returns to the surface through these aquifers (arrows), which empty into lakes, rivers, and the oceans. Under special circumstances, groundwater can even flow upward in artesian wells. The flow of groundwater is much slower than runoff, with speeds usually measured in centimeters per day, meters per year, or even centimeters per year.

precipitation |
|

transpiration |