|
|
. |
Scanning Modes
PPI and RHI
The two main types of scans used in meteorology are the Plan
Position Indicator (PPI) and the Range Height Indicator (RHI) scans.
|
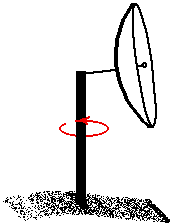
Plan Position Indicator (PPI):
When scanning in PPI mode, the radar holds its
elevation angle
constant but varies its azimuth angle.
The returns can then be mapped
on a horizontal plane.
If the radar rotates through 360 degrees, the scan is
called a "surveillance scan". If the radar rotates through less than 360
degrees, the scan is called a "sector scan". |
|
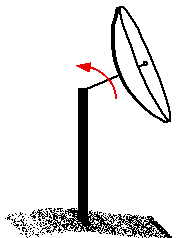
Range Height Indicator (RHI):
When scanning in RHI mode, the radar holds its
azimuth angle
constant but varies its elevation angle.
The returns can
then be mapped on a vertical plane. The elevation angle normally is
rotated from near the horizon to near the zenith (the point in the sky
directly overhead).
|

target location
|
|

radial velocity
|
|



