|
|
. |
Cyclones
bringing clouds and precipitation
A cyclone is an
area of low pressure around which
the winds flow counterclockwise
in the northern hemisphere. Since a cyclone is also known as a
low pressure center,
moving in any
horizontal direction away from the "Low" will result in increasing
pressure.
Air converges into a
low pressure center
which causes air to rise. The
rising motion may produce
clouds and precipitation. Different precipitation types include
rain and
thunderstorms in the summer and
fall seasons, to rain, thunderstorms, and even snow
during the winter.
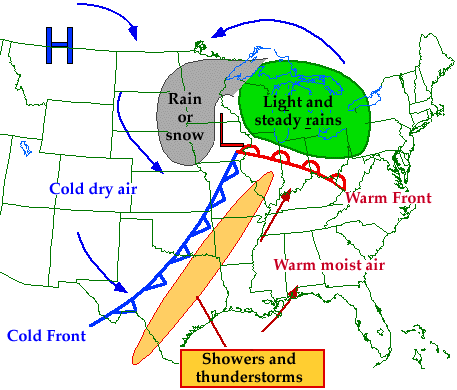
A low is represented on a weather map by a red "L".
As a cyclone approaches, the likelihood of
clouds and precipitation increases.
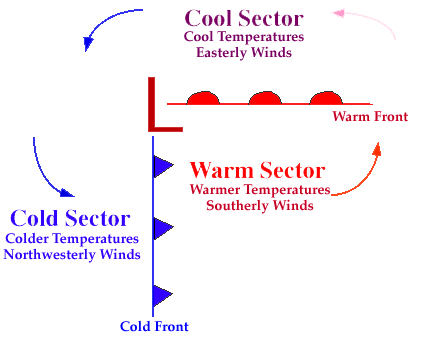
Winds flow counterclockwise
around a
low pressure center
in the northern hemisphere and
temperatures are dependent upon the location relative to the low.
Southerly winds associated with an approaching cyclone are likely to result
in warmer temperatures while northerly winds found on the
backside of a low, or once a low has passed through, typically result in
a cooling trend.

anticyclones
|
|

cold fronts
|
|



