|
|
. |
Cyclones and Fronts
the development of freezing rain
In most cases, freezing rain results from
the process of warm moist air
"overrunning" colder air.
Perhaps the most common overrunning scenario occurs as warm moist
air flows up and over a warm front
associated with a midlatitude cyclone.
The rising air cools, the water vapor
condenses,
producing a narrow band of freezing rain ahead of the front. This
band is typically less than 50 kilometers (30 miles) wide and
is represented by region #1 (shaded in orange) in the diagram below.
This band is often wrapped around and behind the
low pressure center by
counterclockwise winds flowing around
the cyclone. Some of the most devastating ice storms
occur in association with this narrow band of freezing rain.
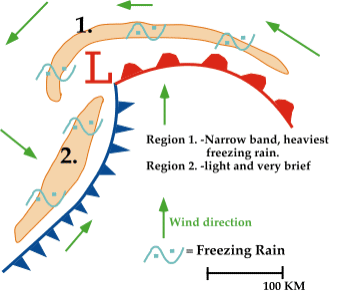
A second area of freezing rain is typically found behind the
cold front, (region #2 shaded in orange in
the diagram above). Freezing rain develops as
southerly winds at upper levels push warm moist air up and over the
cold front, producing precipitation that falls
into the colder air.
Freezing rain associated with the cold
front is usually very light and scattered,
and in rare cases, even observed ahead of the front.
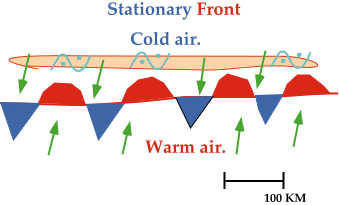
Stationary fronts can be
associated with the production of freezing rain.
A stationary front separates cold air to the
north from warm moist air to the south. Freezing rain develops as
upper-level winds (typically
light and southwesterly) push warm moist air over the colder air north of the
stationary front, producing a narrow band of freezing rain on the cold side
of the frontal boundary.
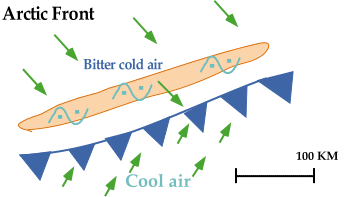
Arctic air masses are typically very shallow and have been known to
produce devastating ice storms.
Behind a cold front,
the air mass is maritime polar (mP), but behind an
Arctic front, the air mass
is continental polar (cP).
As Arctic air advances, it lifts the
warm moist air (ahead of the front),
producing precipitation that falls into the Arctic air.
Sometimes, a band of freezing rain wider than 50 kilometers
develops in association with an Arctic front.
processes
|
|

pressure features
|
|




