|
|
. |
Forecasting Freezing Rain
the importance of temperature profiles
Freezing rain is one of the most difficult events to forecast.
The smallest variations in temperature (even only tenths of a degree)
can mean the difference between
rain,
freezing rain,
sleet or
snow.
Freezing rain occurs less frequently than
other winter weather events and
falls in very narrow bands, usually not more than 50 kilometers wide.
When attempting to forecast a freezing rain event,
sounding data is very useful
for examining vertical temperature profiles of the atmosphere, which
are indicative of what type of precipitation (if any) will likely occur.
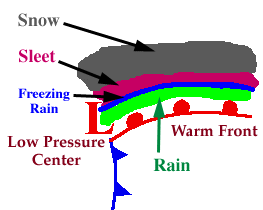
There are four types of soundings associated with the
four different types of precipitation (mentioned above).
In the following diagrams, the blue line represents the temperature profile
of the atmosphere and the black line represents the 0C isotherm (a line of
equal temperature).
When the blue line is to the right of the black line, it means the atmospheric
temperature is warmer than 0C, but when the blue line is to the left of the
black line, it means the atmospheric temperature is colder than 0C.
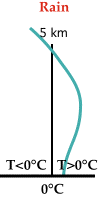 |
Rain:
The entire temperature profile near the ground is above freezing so all
ice particles completely melt and reach the ground as rain. |
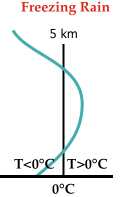 |
Freezing Rain:
A shallow layer of cold air lies below a layer of warmer air,
which completely melts all ice particles as they pass through.
When the raindrops enter the shallow layer of cold air, they supercool and
freeze instantly on contact.
|
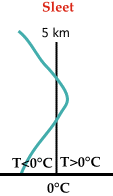 |
Sleet:
The warm layer is very shallow so ice crystals only partially melt as they
pass through.
Once they enter the cold layer below, they freeze again and strike the
ground as ice pellets, or sleet. |
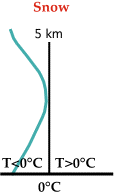 |
Snow:
The entire sounding is completely below freezing so the
precipitation reaches the ground as snow. |
Conditions
|
|

classic sounding
|
|






