|
|
. |
The States of Water
solid, liquid, gas
Water is known to exist in three different states; as a solid, liquid or
gas.

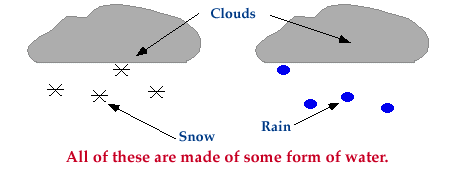
Clouds, snow, and rain are all made of up of some form of water.
A cloud is comprised of
tiny water droplets and/or ice crystals, a snowflake is an aggregate of many
ice crystals, and rain is just liquid water.
Water existing as a gas is called water vapor.
When referring to the amount of moisture in the air,
we are actually referring to the amount of water vapor.
If the air is described as "moist", that means the air contains
large amounts of water vapor.
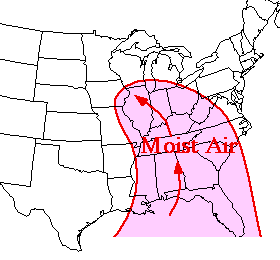
Common sources of moisture for the United States are the
warm moist air masses that flow
northward from the Gulf of Mexico and western Atlantic Ocean as well as the
moist Pacific air masses brought onshore by the westerlies.
Clouds, Precipitation
|
|

relative humidity
|
|