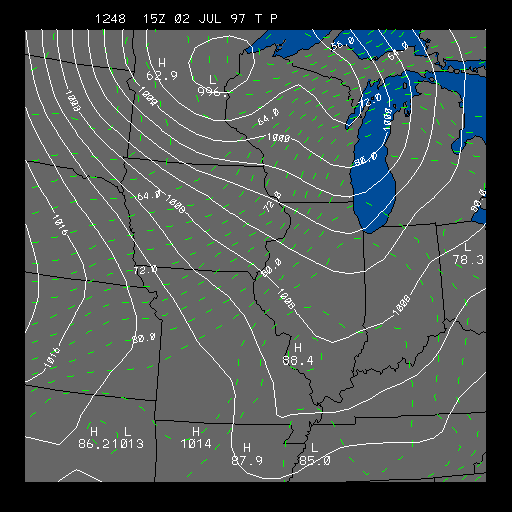
Latest Pressure and Temperature Distribution
This panel depicts sea-level pressure and temperature lines. This chart is useful for finding fronts and high and low pressure systems.
The solid white contours represent pressure contours (isobars) in millibars. The Isobars have a contour interval of four millibars. The wind speed is directly related to the distance between the isobars. The closer the isobars are together, the stronger the pressure gradient, and the stronger the wind.
The dashed green lines represent isotherms. Isotherms are lines of equal temperature. The contour interval of the isotherms is two degrees Fahrenheit. From the chart above you can sometimes find warm and cold fronts. Fronts are usually located where temperature changes drastically over a short distance.
When pressure contours are perpendicular to isotherms it means it is either getting warmer or colder. By knowing that winds flow counter-clockwise around a low and clockwise around a high, one can usually see whether there is warming or cooling going on. Usually when the winds are from the south, and you have isotherms (temperature lines) perpendicular to the isobars (pressure lines) you have warm air advection (warm air moving up from the south). The opposite is true if you have winds from the north and isotherms perpendicular to isobars. In that case you have cold air advection (cold air coming in from the north) going on.
On July 2, 1997 Michigan, Indiana, and Ohio were rocked with over a dozen tornadoes in which eight people were killed. This image shows the strong front over eastern Illinois in the morning preceding the tornado outbreak. The front is located at the leading edge of the tightly packed isotherms. It is also located in the pressure trough. The isotherms are perpendicular to the isobars behind the front so there is strong cold advection occurring.
For more information on how pressure affects the weather go to our pressure module
24 Hour Totals |
|

dew point |