|
Pressure Activity
teacher guide
1) The units are inches of Mercury ("Hg),
atmospheres (atm), kilopascals (kPa)
and millibars (mb). Millibars is the unit used
most by meteorologists.
2) Decreases because the
number of molecules
above a surface decreases with height. Since there are fewer air molecules
at higher levels to exert a force on a surface, the pressure
at higher levels is less than at lower levels.
3)
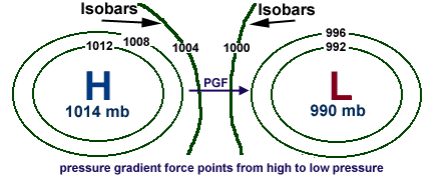
A blue "H" represents a high pressure center.
A red "L" represents a low pressure center.

4) A low pressure center should be labeled
beneath the left column because there are fewer air molecules in that column
to exert a force on the surface below. Therefore, the pressure at the surface
is lower (than for the right column).
5) The green contours are isobars and they
are lines of constant pressure.
6) Working with current weather data,
so no answer key is available.

introduction
|
|

air masses
|
|



