|
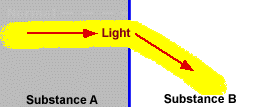 |
Refracted light is light that bends as it travels from one substance to another. |
The amount of refraction that occurs depends upon the density of the
substance and the angle at which the light is entering the substance.
Photograph by Bob Rauber |
The refraction of sunlight (or moonlight) by ice crystals can result in a number of beautiful optical effects like halos which are produced when sunlight or moonlight is refracted by the pencil-shaped ice crystals of cirroform clouds. |
Photograph by Bob Rauber |
Sundogs are the result of sunlight refracted by slowly falling, hexagonal-shaped ice crystals. |
Light refraction is also responsible for other unique effects, like
bending the rays of a setting sun to give it
an elliptical, "flattened-out" appearance.
|