|
|
. |
Diffraction of Light
light bending around an object
Diffraction is the slight bending of light as it passes around
the edge of an object. The amount of bending depends on the
relative size of the wavelength of light to the size of the
opening. If the opening is much larger than the light's wavelength,
the bending will be almost unnoticeable. However, if the two are
closer in size or equal, the amount of bending is considerable,
and easily seen with the naked eye.
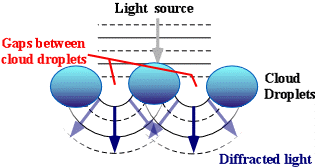
In the atmosphere, diffracted light is actually bent around atmospheric
particles -- most commonly, the atmospheric particles are tiny water
droplets found in clouds. Diffracted light can produce fringes of light,
dark or colored bands. An optical effect that results from the diffraction
of light is the silver lining sometimes found around the edges of clouds
or coronas surrounding the sun or moon. The illustration above shows how
light (from either the sun or the moon) is bent around small droplets in
the cloud.
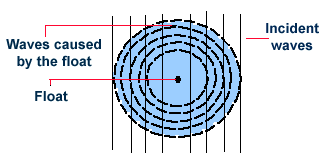
Optical effects resulting from diffraction are produced through the
interference of light waves. To visualize this, imagine light waves
as water waves. If water waves were incident upon a float residing
on the water surface, the float would bounce up and down in response
to the incident waves, producing waves of its own. As these waves
spread outward in all directions from the float, they interact with
other water waves. If the crests of two waves combine, an amplified
wave is produced (constructive interference). However, if a crest of
one wave and a trough of another wave combine, they cancel each other
out to produce no vertical displacement (destructive interference).
This concept also applies to light waves. When sunlight (or moonlight)
encounters a cloud droplet, light waves are altered and interact with
one another in a similar manner as the water waves described above.
If there is constructive interference, (the crests of two light waves
combining), the light will appear brighter. If there is destructive
interference, (the trough of one light wave meeting the crest of another),
the light will either appear darker or disappear entirely.
Refraction
|
|
air, dust, haze
|
|



