|
|
. |
Pressure Gradient Force
points from higher to lower pressure
The change in pressure
measured across a given distance
called a Pressure Gradient.
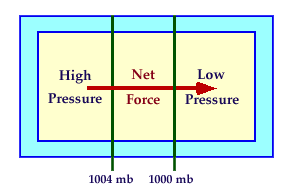
The pressure gradient creates a net force that is directed from
higher to
lower pressure and is called the Pressure Gradient Force.
[Image: animation of air directed by the pressure gradient force (35K)]
This force is responsible for triggering the initial movement of air,
which in turn leads to the development of wind. As air increases in velocity,
it is deflected by the Coriolis Force.
|
