|
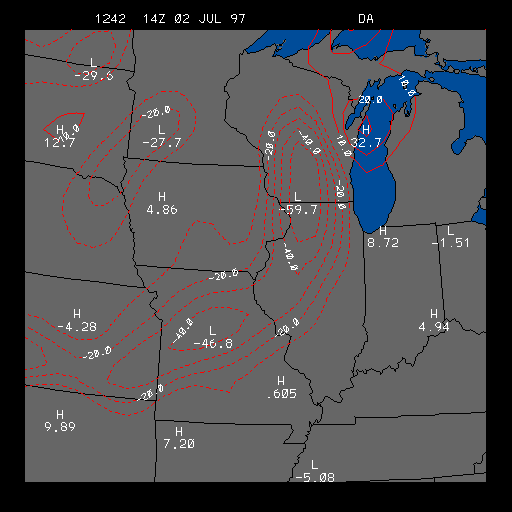
Example Surface Dew point Temperature Advection Image
This is the Surface Dew point Temperature Advection image which is useful for
finding areas of positive and negative dew point temperature advection.
Positive advection areas are outlined in solid lines and indicate that the dew point temperature is increasing due to advection. Negative advection areas are outlined in dashed lines, and indicate that the dew point temperature is decreasing due to advection. Both advection areas are contoured in intervals of 10 degrees Fahrenheit per day, so a positive advection outline of 20 indicates that if positive advection was to continue at the present rate for 24 hours, the dew point temperature would warm by 20 degrees Fahrenheit in that region.
At a given temperature, the higher the dew point temperature, the more moisture in the air. By taking dew point temperature advection to be analogous to moisture advection, we can say that when there is positive dew point temperature advection, there is also positive moisture advection.
Severe weather analysts pay close attention to the distribution of low-level moisture. Areas rich in moisture help to destabilize the atmosphere, which in turn support the generation of strong updrafts. If the updrafts occur near areas of positive dew point advection, the potential for significant thunderstorm development increases.
The example image above shows an area of strong negative dew point advection located in Wisconsin, Illinois and into Missouri. This negative dew point advection area is due to a cold front that was passing through those areas at the time of this image. This image clearly shows how much drier the air was behind the cold front than ahead of the cold front.

temp. advection |
|

3hr dew pt & wind |




