|
 |
Currently the US operates two geostationary satellites (GOES-8 and GOES-10) in geostationary orbit over the equator. |
| Image provided by GOES Mission Overview |
The GOES-8 is located at 75 west longitude above the equator and it covers North and South America and most of the Atlantic Ocean. The GOES-10 is also located above the equator at 135 west longitude and it monitors North America and the Pacific Ocean basin.
 |
 |
| Images provided by: Satellite Coverages and Orbits (NCAR) | |
Both satellites carry imager and sounder instruments. The three-axis, body stabilized spacecraft design enables the sensors to image clouds, monitor earth's surface temperature and water vapor fields, and sound the atmosphere for its vertical thermal and vapor structures. GOES-8 and GOES-10 also introduce two new features: flexible scanning that allows small-area imaging plus simultaneous and independent imaging and sounding, allowing continuous gathering of data from both instruments.
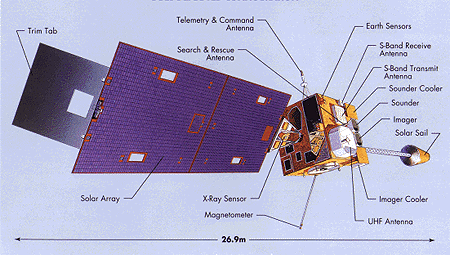
Image provided by: GOES-I/M Brochure
The components of a deployed GOES satellite are labeled in the diagram above. The main body has dimensions of 2.0 x 2.1 x 2.3 meters (m) and when the solar array deployed, the satellite is 26.9 meters long. The craft weighs 2104.7 kilograms (kg) and has a minimum lifetime of 5 years. GOES-8 was launched on April 13, 1994 and GOES-10 followed on May 23, 1995. GOES-10 launched on April 25, 1997 and has replaced GOES-9.
Text Provided By: GOES Mission Overview

history of GOES |
|

imager |




