|
|
. |
Common Freezing Rain Sounding
useful when forecasting freezing rain
Soundings are the most important tool for identifying potential
freezing rain regimes. Three types of soundings can lead to
freezing rain and the most common
consists of a shallow layer of cold air at the surface with a depth of about
600 meters (1,800 feet).
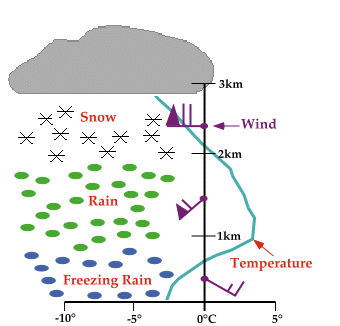
Above the cold air
is a layer of warmer air
with a depth of about 1,400 meters (4,200 feet).
Winds near the surface are usually east or
southeasterly, then veer around to the southwest in the warm air, and
finally become westerly in upper levels.
The sounding given above represents only an average case.
|
