|
|
. |
Atmospheric Pressure
force exerted by the weight of the air
Atmospheric pressure is defined as the force per unit area exerted against a
surface by the weight of the air above that surface.
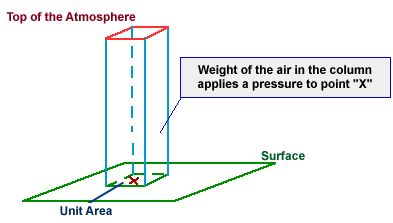
In the diagram below, the pressure at point "X"
increases as the weight of the air above it increases.
The same can be said about decreasing pressure, where the pressure at point "X"
decreases if the weight of the air above it also decreases.
Thinking in terms of air molecules, if the number of air molecules above
a surface increases, there are more molecules to exert a force on that
surface and consequently, the pressure increases.
The opposite is also true, where a
reduction in the number of air molecules above a surface will result in a
decrease in pressure.
Atmospheric pressure is measured with an instrument called a "barometer", which
is why atmospheric pressure is also referred to as barometric pressure.
|
