|
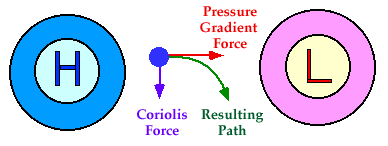
An air parcel initially at rest will move from high pressure to low pressure because of the pressure gradient force (PGF). However, as that air parcel begins to move, it is deflected by the Coriolis force to the right in the northern hemisphere (to the left on the southern hemisphere). As the wind gains speed, the deflection increases until the Coriolis force equals the pressure gradient force. At this point, the wind will be blowing parallel to the isobars. When this happens, the wind is referred to as geostrophic.
|