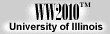
|
Forecast Tip:
When forecasting temperatures, look at the temperatures upstream from the
station for which you making a forecast.
If they are warmer,
that means warmer air is being transported towards your station and the
temperature should rise. Put in another way, if there is warm advection
occuring at a given station, expect the temperatures to increase.
In contrast, if cold advection is occurring at a given station,
expect the temperatures to drop.
Temperature advection refers to change in temperature caused by movement of air by the wind. Forecasting temperatures using advection involves looking at the wind direction at your forecasting site and the temperatures upstream (in the direction from which the wind is blowing).
For example, consider the two cities below. Assume that a
temperature forecast is being made for the northern station, which has a
reported temperature of 45 degrees.
The northern station is cooler than the southern station,
but the wind directions
are the same, out of the south.
The wind is, in effect, blowing from the southern station towards the
northern one. Over time, the wind will transport the warmer air
located at the southern station towards the northern station (into a region
of colder air), so expect
the temperature at the northern station to rise. This process is called
warm advection.
When colder air is being transported by the wind into an area of warmer air,
this is known as cold advection.

highs and lows |
|

snow cover |




