|
Cold advection is the process in which the wind blows from a region of cold air to a region of warmer air. The following animation depicts a very simple example of cold advection. The horizontal lines are isotherms in degrees Fahrenheit and the arrows represent wind vectors. Winds are blowing from a region of cold air to a region of warmer air, which results in cooling of the warmer region. As the cold advection persists, temperatures in the warmer region will begin to decrease as the colder air moves into the region of warmer air.
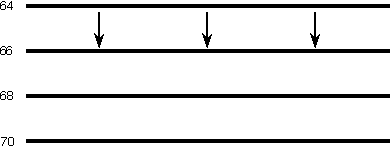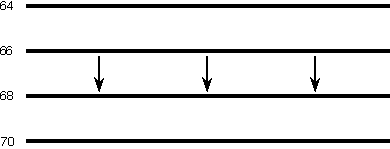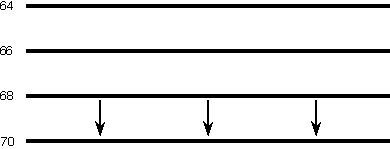
Animation by: Van Dorn
The net result of cold advection is to make a region cooler. The animation below shows (in a very general sense) how cold advection can lead to sinking motion. Cold advection is occurring in Figure A while Figure B shows a vertical cross section through the region of cold advection. In Figure B, the horizontal lines are isobars and the arrows represent wind vectors. It is important to note that Figure A is along the ground and that Figure B is from the ground up to a higher level in the atmosphere, directly above the region of cold advection.

Animation by: Van Dorn
With the onset of cold advection (Figure A), the isobar in Figure B starts to bend downward since colder air is more dense and occupies less room than warmer air. The bending of the isobar due to cold advection creates a localized area of low pressure ("L" in Figure B"), thus altering the pressure gradient force. As air moves from the regions of high pressure ("H" in Figure B) to the local region of lower pressure, air is pushed downward from above, which is the sinking motion that is caused by cold advection.

advection |
|

warm advection |




