|
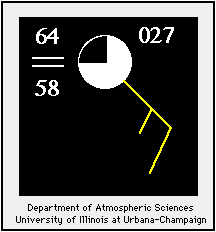
Observed Winds
represented by wind barbs
The symbol highlighted in yellow (in the diagram above)
is known as a "Wind Barb".
The wind barb indicates the wind direction and wind speed.
Wind barbs point in the direction "from" which the wind is blowing.
In the case of the diagram below, the orientation of the wind barb
indicates winds from the Northeast.
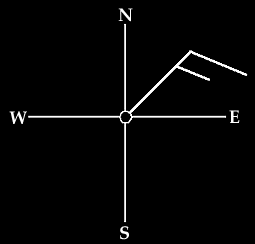
The term easterly means that the winds are from the east.
In the example above, the winds are out of the northeast, or
northeasterly.
On the otherhand, the term "eastward" means that the winds
are blowing towards the east.
Wind speed is given here in the units of "knots" (knt).
A "Knot" is a nautical mile per hour.
| 1 Knot = 1.15 Miles Per Hour (MPH)
1 Knot = 1.9 Kilometers Per Hour (KM/HR) |
Each short barb represents 5 knots, each long barb
10 knots. A long barb and a short barb is 15 knots, simply by adding
the value of each barb together (10 knots + 5 knots = 15 knots).
If only a station circle is plotted, the winds are calm.
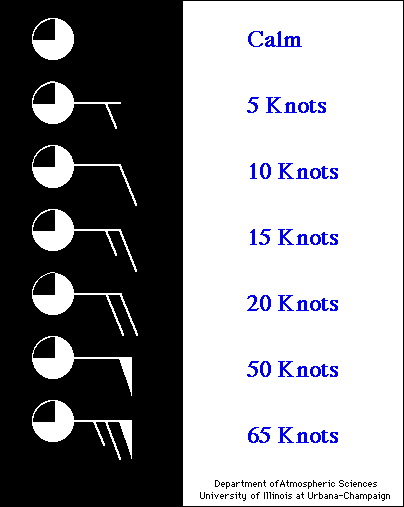
Pennants are 50 knots.
Therefore, the last wind example in the chart below
has a wind speed of 65 knots. (50 knots + 10 knots + 5 knots).

pressure
|
|
Contours
|
|




